With howling westerly winds and in freezing rain, the unforgiving waves push ships closer to the treacherous rocks of the merciless Cornish coastline. The crew has travelled miles with precious cargo, desperately trying to right their course with no modern navigation. In an attempt to save the vessel and themselves, they begin to throw goods overboard.
Countless lives, ships and cargo have been lost along the Cornish coastline. Wrecking – a well-known yet perhaps mythical aspect of Cornish history – is often associated with the deliberate act of luring ships to shore by poor lower-class tenants. In comparison, the term ‘wrecker’ relates more closely to residents who retrieved the goods washed ashore, especially as the finder could claim one-half of their value as salvage. It was this lucrative right to the wrecked goods that often led to zealous legal disputes between neighbouring landowners of coastal manors (see footnote 1).
This is a topic with many facets, too broad to cover in their entirety, but this blog hopes to provide an interesting insight into the ‘right of wreck’ along parts of the Cornish coast.
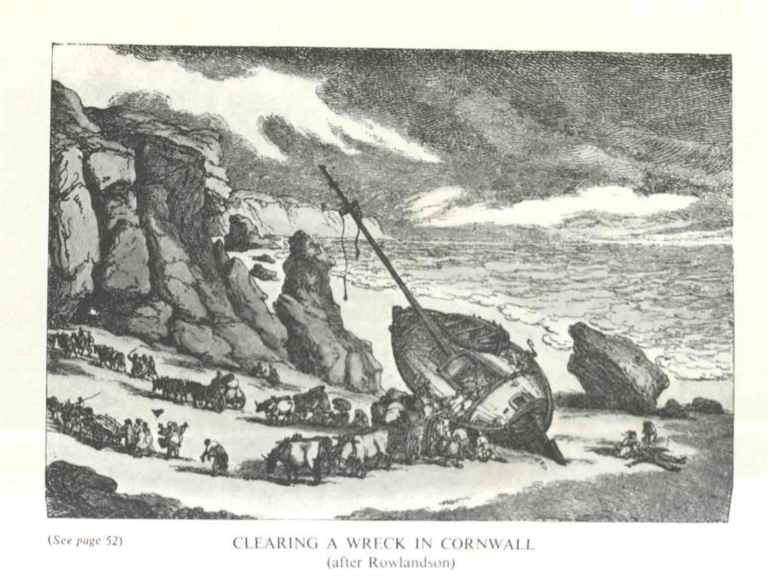

The ancient right of wreck
The right of wreck could be considered one of the earliest maritime franchises granted by the Crown (see footnote 3) to local landowners holding manors or hundreds. Hundreds were larger units of land in which manors could be located. All the hundreds in Cornwall originally belonged to the Duchy, except the Hundred of Penwith. The right of wreck franchise would entitle landowners to a combination of the flotsam, jetsam and ligan (see footnote 4) but did not necessarily include ownership of the land or sea. At any one time, different landowners could hold different rights along the same part of the coast … what could possibly go wrong!
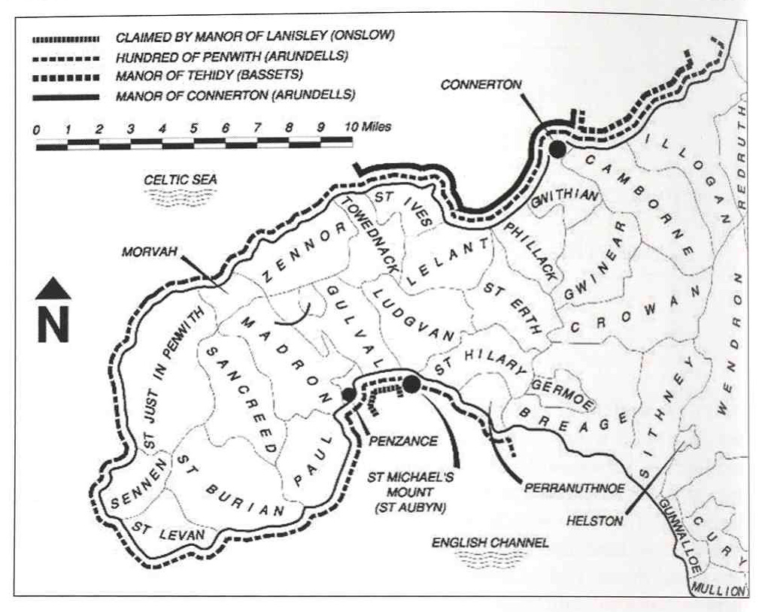
Disputing landowners
Wreck records provide an intriguing insight into the complicated and delicate relationship of neighbouring manorial lords. The manor of Tehidy (owned by The Bassets) sat within the Hundred of Penwith (held by the Arundell family). Perhaps among the shrewdest and wealthiest lords in Cornwall during 18th century, the Bassets frequently disputed the right to wreck of the Arundell family and fought ardently to prove their entitlement to wrecks within the manor of Tehidy. Surviving archive material documents the two families disputing their rights for nearly 100 years, often citing a lack of decree to either’s claims. It seems due to a lack of evidence that the families’ last wreck encounter was thrown out of court and the Bassets enjoyed all royalties within the manor ever since.
The Arundells were often involved in further disputes with other landowners, the details of which can be found on the Kresen Kernow website.

A great fish and Civil War dispute
Amongst the turmoil of the Civil War, a great fish was washed ashore near Mevagissey, within the manor of Bodrugan. A series of letters from Richard Edgcumbe at Bodrugan to his brother Colonel Piers Edgcumbe documents the legal dispute with the admiralty over the great fish. The great fish (whale) is described in vivid detail as ‘so odious to the smell as that I could not endure to come near it’ (see footnote 6). Its description includes a length of 72 feet, girth by fins 28-30 feet, its head 13 by 8 feet, with fins 5 by 3 by 2 feet, and its eyes no bigger than an ox’s.

Richard first writes to his brother on 16 December 1647, notifying him that a whale has been cast ashore and, as he has the title and privilege of wrecks, he seized it on his behalf, even though there is already strong opposition from the Admiralty. Four days later, he writes that John St Aubyn, Vice Admiral for Cornwall, has come to seize the whale and states he ‘could not be satisfied till he had the sight of the patent’ (see footnote 7). One does wonder if this was merely just a case of right of wreck or, as the Edgcumbes were staunch Royalists and Aubyn was a Colonel in the Parliamentary army, perhaps this whale signified something more.

With the aid of legal counsel, the brothers made a defence, outlining the total cost of the endeavour while refuting the claim that it was a whale (more of a great fish) and underlining their right of wreck (see footnote 8). It seems that the onset of the Second Civil War may have saved the Edgcumbes as the Admiralty’s attention turned elsewhere and we hear nothing more of the case except a set of jaw bones sit at Cotehele, although their origin is unknown (see footnote 9).

A fine for clandestine wine
Presentments are formal statements or evidence provided to a manorial court and these documents provide an insight into the relationships between the lord and their tenants. Walking a fine line between legal and illegal wrecking, lords of the manor held great sway over their tenants, who usually informed manor officials of a wreck. The tenant who found the wreck would receive half the goods and the other half would go to the lord. The amounts collected from wrecks were highly unpredictable but, when large vessels were lost, the profits could be spectacular.
Two such tenants on the manor of Winnianton perhaps decided that the risk of a fine from the lord was worth ‘clandestinely’ carrying off about 54 gallons of wine from Gunwalloe church cove, with the empty cask being presentment at court. In cases of such misdemeanours, the resident lord of the manor handed out fines as punishment.

An unexpected elephant’s tusk
Wreck presentment records can also provide us with a historical snapshot of the trade in goods. Ships travelled great distances, bringing with them cloth, spices, tea, hogsheads of wine, rum, anchors of brandy, sugar, precious jewels and ivory. An interesting wreck find, recorded as being found ashore within the manor of Methleigh, was an elephant’s ‘tooth’ (tusk). The full document, written by the steward of the manor, is dated 31 October 1765 and mentions a French ship thrown ashore under the lands of Trequean, near Rinsey, within the manor. The commercial trade in ivory for piano keys, jewellery, ornaments and works of art was nearing its peak at this time.
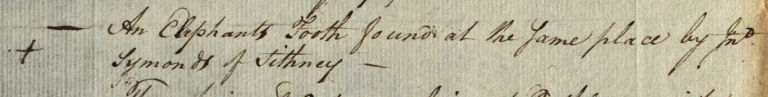
Right of wreck records provide us with a fascinating insight into life on coastal manors, including the relationships between neighbouring lords and their tenants. Localised brushes with manorial law provide us with wider historical insight into maritime and trading history. This blog has only just touched on the topic and if you would like to know more about wreck records and the Manorial Document Project for Cornwall, please contact Kresen Kernow – A home for Cornwall’s archives. You can also learn more about the Manorial Document Register on our website. And finally, if you find yourself walking along the coast and stumble across a piece of sea glass, a buoy, some driftwood, or pick up pieces of plastic washed in with the tide, you might just be a modern-day wrecker!
Further reading
- Catheryn Peace (2010) Cornish Wrecking 1700-1860, Reality and Popular Myth, Boydell Press
- Wreck and Salvage Law: Wreck and salvage law – GOV.UK (www.gov.uk)
- Franchises and manors: Practice guide 13: Official searches of the index of relating franchises and manors – GOV.UK (www.gov.uk)
Footnotes
- Maryanne Kowaleski (2001) The Havener’s Accounts of the Earldom and Duchy of Cornwall, 1287-1356, pp. 23-26, Devon and Cornwall Record Society
- A K Hamilton Jenkins (1932-1934) Cornwall and its People, David and Charles Publishers
- Stuart A Moore, (1888) ‘A History of the Foreshore and the law thereto’; available at: ‘A History of the Foreshore and the Law Relating Thereto: With a Hitherto …’: Stuart Archibald Moore, Matthew Hale , Robert Gream Hall: Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming: Internet Archive
- Christopher Jessel (1998) The Law of the Manor, pp. 264-265, Barry Rose Law Publishers
- Catheryn Peace (2014) ‘The Cornish Arundells and the Right of Wreck’, pp. 209-217, within The Maritime History of Cornwall, edited by Philip Payton, Alston Kennerley and Helen Doe, University of Exeter Press
- ME/2820, Letter from Richard Edgcumbe, treatment of whale washed ashore, 1648, Kresen Kernow
- ME/2821, Letter from Richard Edgcumbe, whale seized by John St Aubyn, 1647, Kresen Kernow
- ME/2833, Account of charges for saving whale washed ashore at Polstreath, Mevagissey, 1648, Kresen Kernow
- Cotehele Journal, Volume, 1, March 2009
Very interesting, my ancestors, the Jago’s, lived on St. Michael’s Mount, owned by the St. Aubyns. They were mariners too.
Even a sheltered coast like that of the Lincolnshire Wash received washed-up whales in the 14th century, one of which attracted a long list of men who carried it off in contravention of the right of wreck. That belonged to the local Lord, Ebulo Lestrange, whose wife was Alice Countess of Lincoln. A 19c interpreter thought that Ebulo had bathing rights, that being his translation of balena, eventually corrected to whale.
Deliberate wrecking of vessels using false lights is pure myth, there is no hard evidence to prove that it ever happened in Cornwall or I suspect anywhere else. It was government propaganda to turn public opinion against smugglers who were depriving the government of much revenue. How ever would any intelligent sea captain be fooled into believing that a few lanterns seen on cliff tops could be a harbour or safe haven, it’s ridiculous. And how would these “wreckers” know in the dark that a vessel seen offshore was carrying valuable cargo and not be a returning troopship. The suggestion that Cornish coastal people deliberately wrecked ships and murdered crew is a vile slur, many Cornish villagers risked their lives to rescue sailors in trouble and Henry Trengrouse actually invented a rocket line device after watching Cornish people trying to save men off HMS Anson.
Wrecking in the sense of looting i.e. taking goods washed ashore yes that is true and regarded by folk as a bounty from the sea to help their miserable lives. Catheryn Pearce’s book is highly recommended
Very Informative and fascinating too.
All humans, irrespective of social status would not spare making extra money. Of course it was justified through claims supported by laws, convention and mere happenstance maybe!
What a hidden chapter in maritime history . An excellent article.
Early civilisation often evolved along the coasts, the areas have always been bountiful sources of resources fish shellfish etc and of course those societies considered that to be theirs.
Kings came along and decided it was theirs, they took it.
Sometimes they sold that right either to local lords or gave it to the local population like in the Cinque Ports region.
Once those kings or rulers had given that right away they could never again give it to anyone else
A fascinating subject
How much truth / rumoured history is the basis for the story ‘Moonfleet’?