The census is an ambitious data-gathering exercise that aims to record details about the population as a whole. This creates a huge quantity of information that has to be collected, sorted and studied. But how, exactly, does this happen?

Over the years, the census and its systems have changed and evolved. From the Victorian clerks who waded through information manually to modern computers that process data at the click of a button – in this post, we look at how new ideas and new technology have changed the face of the census.
Collecting information
The first census was taken in 1801, in an attempt to get a better understanding of the UK and the challenges it faced. To start with, the census collected information about neighbourhoods rather than individuals. Officials called enumerators were each put in charge of an area that they had to research, recording information such as how many houses were occupied, how many people had recently been born, and in what sorts of industries people in the community worked.
In 1841 this all changed when it was decided that every single person should be recorded. This was an ambitious aim, but it meant that the data collected would be far more detailed and accurate. In order to collect this huge amount of information, a form was delivered to every home and the head of the household was told to fill it out. To start with, this form asked for every person’s name, age and occupation. New questions were added later, such as place of birth and marital status.
Once the form was completed, the enumerator came to collect it. Some families struggled with the form as they were unable to read or write. If this was the case, the enumerator could help them, but many also turned to literate friends or neighbours for assistance – sometimes in return for payment.
Some enumerators had to walk a very long way to collect all of these forms. In cities, where people lived in close proximity, their area might be quite small. But in rural communities, homes were sometimes very far apart. In 1861, one official working in rural North Wales recorded that it was 34 miles between the first and last houses in his district. Some enumerators even sketched a map, showing exactly where they had been.
But the enumerators’ work was not done yet. They then had to transfer all this information into books, by hand. Sometimes they had help with this. In 1871, one enumerator noted that he had help from ‘an old lady who is upwards of 73 years of age’.
In the case of institutions such as workhouses, prisons and hospitals, individuals’ information was recorded in a special enumeration book. This was done by an official from the relevant institution who was designated as an enumerator.
Today, if you search the census for information collected between 1841 and 1901, you will find the records written up by the enumerators. The forms filled out by each household were largely discarded.
However in 1911 this changed. Instead, the individual records were kept. This is because new technology meant that the schedules could be tabulated without the need for transcription. This is good news for family historians today, as it means you can often see an example of your ancestors’ handwriting.
Cards and computers to the rescue
As time went on and technology developed, it became possible to collect and process census information in clever new ways. In 1911, the census data was stored on a series of cards with holes punched in them. These were then fed into machines that processed and collated the information far more quickly than it could be done by hand.
In 1961 there was another leap forward. Computers were used to process data for the first time, allowing experts to interpret information far more quickly. Over the following decades the computers used became increasingly advanced, until in 2011 when there was an even bigger change. It now became possible for people to fill in the census form online. About 16% of people recorded their information on the internet.

For the 2021 census, no paper forms will be sent out, unless they are specially requested. Instead, everyone will be sent a code and encouraged to record their information digitally.
Advertising the census
The census only works if everyone takes part, so it is very important to make sure that everybody knows how to complete their return. Over the years, the government has tried many ways of advertising the census. In the 19th century there was extensive publicity in newspapers, where official notices appeared. In the 20th century, officials turned to film. Some of their information films make for an amusing watch!
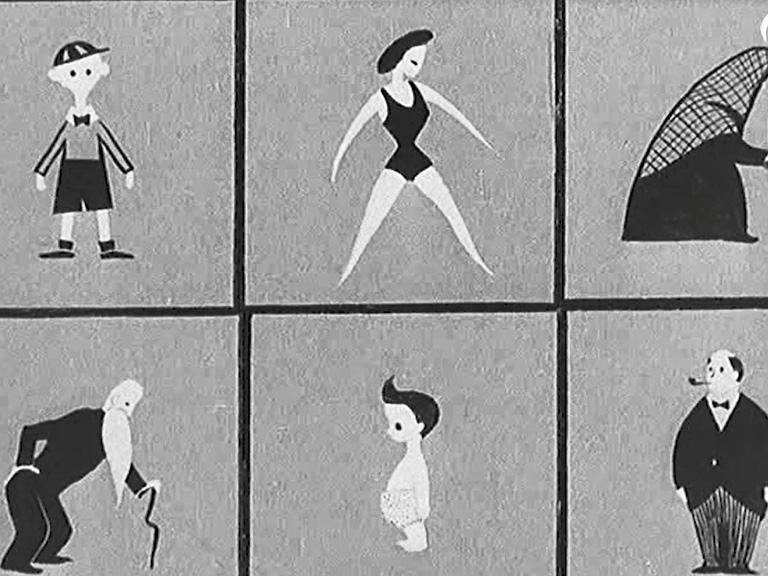
‘Your answers will draw the picture of the nation and its needs!’ This was what an advert from 1951 told viewers, demonstrating what the form looked like and using cartoons to help explain how it works. It was especially important to advertise this census, as it was the first to take place in 20 years – in 1941, the census was cancelled as Britain was in the middle of the Second World War.

Though there was no census in 1941, there was still time to raise wartime spirits with some humour. In this film the keepers at a zoo are shown taking a census of their animals. From bears to fleas – no creature is left out!
In 1961 the message was ‘Everybody counts!’ and adverts explained that census guidance was now available in several different languages – from Urdu to Arabic. One of the public information films explained that nobody would be left out, telling viewers that patients in hospitals, nuns in convents, people on boats and even those in prison would all be counted.
‘We’re all to be counted again! Somerset House and 80,000 enumerators are on the job! Millions of films are being distributed, and most of them, of course, are in English. They’re printed in other languages too for the many races in Britain – and everybody counts!’
Even though the census continues to change and evolve, the message is still the same in 2021 – everybody counts!
Dr Anna Maria Barry is a writer, historian and curator. She works on 19th-century culture.
Why do officials always assume that everyone has a computer? Out of 5 neighbours, only 2 of us have and use a computer, mainly for e-mails and looking up things for our family history.
What an interesting piece, beautifully written with amazing images. I was one of the enumerator about 30 years ago, visiting homes to drop, collect or help complete the forms them too. Didn’t have Fitbit at the time, but covered some mileage. Woorah for technology, how many trees have we saved and the environment. Wonder what it will look like in 2031.
This year the Census in Scotland is not being held until next year due to Coronavirus. Actually the 1911 Census returns for Scotland were not the original forms filled out by individuals as these were transferred onto schedules and the original forms do not survive. The introduction of the use of computers for the 1961 Census raised the issue of Census confidentiality and the information be used for ‘Big Brother’ purposes and that view still prevails, why does the Government need to know the names of the people living at an address. In addition in the 1971 Census it was proposed to include a ‘race’ question which after public uproar resulted in the question being removed. The 2011 Census and this one will again not ask [people not where they were born, reducing the value of information to future family historians.
The 2021 census is likely to be less than complete becasue it has gone online. The extent of digital povery has been strarkly revealed during the pandemic lockdown. Broadband isn’t available nationwide and as home schooling revealed, some families rely on a single smart phone for their digital connectivity or have no connectivity at all. Although the records for better-off neighbourhoods are likely to be complete, those living in the the many areas where inequality, deprivation and poverty prevail may well be unable to complete the census. Those unable to complete the census will then face a £1,000 fine, which is rather like fining the homeless for sleeping on the streets, as has already happened. And as for requesting paper forms, those needing them are likely to have more urgent priorities.
Great article. I was an enumerator in 1991 and it was certainly an experience, but I found it very enjoyable.
One household asked if they should include their pet duck kept in the garden! Another older person only completed the first page of the forms. She said she did not think she needed to fill out all of them and so I assisted her to complete the rest. When asked for an answer to the question `sex` she replied “not for a very long time”!
It took one day to deliver all of the forms prior to census day and a week to collect them in after census day because people had not completed them correctly. I had two households that refused to comply so had to pass them on to my boss for further investigation . Plenty of cups of tea were offered and it was a great experience that I was able to pass on to my family history course students in my work.
I recall being visited by an enumerator during the sensus of 1971 and keeping him stranded for a long time because we insisted that I (a 19 year-old woman!!!) was effectively the Head of the Household as my boyfriend was unemployed at the time and therefore not earning (except a bit of ‘dole’ money). He was very reluctant to agree with our request…..
I was an enumerator for the 1981 census – a job I enjoyed very much. It was a real eye-opener as to how people lived and how many people thought it wasn’t important. The best time to collect the completed forms was calling between 7.30 – 8.30am! The census is such an important source for all manner of future planning. It is also a major research tool for family and local historians. Looking forward to seeing the 1921 census next year.
The census does help your family research. But the earlier ones often state labourer when they could have been farm labourer. A street maintenance labourer, a factory worker – just a labourer. Etc which doesn’t give you much idea of what your family actually worked in.
So I’ve brought maps of the areas I’m more interested in which shows the industry or farm land etc.
Family in Calne Wiltshire seemed to move about in wiltshire across the years but still state labourer. In fact the area was farming mainly so the moving around could have been due to need of farms in the area or not enough work so younger male moved where he could find work. But it’s mainly conjecture.